Shop
Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation
£375.00
Our Courses Scale Perfectly To Any Device
About our Online Self-Study Course
The Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course has been designed to give you a complete technical overview of all aircraft systems. The course covers all mechanical and avionics systems, This self–study online Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course will take approximately 40 hours of study. Students must pass the multi-choice question at the end of each ATA chapter before the next ATA chapter is unlocked. A completion certificate is issued on successful completion of the course.
Our General Familiarisation courses are produced to a minimum of ATA 104 Level 1 and EASA Part 66 Level 1 knowledge levels and course completion time will be approximately 40 hours. This information is stated on the certificate.
You have 12 months from enrollment to begin the course and after starting, 6 months to complete the course. You have a further 90 days to review the course after completion.
Click on the DESCRIPTION below for course syllabus and more details. Please click here to view our sample course
When checking out, please ensure you use the student’s name. To enroll multiple students in the same course, please make separate transactions or contact us for team discounts
Description
BOEING 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 GENERAL FAMILIARISATION COURSE
ABOUT
Our Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course meets ATA 104 Specification Level I: General Familiarisation; A brief overview of the airframe, systems and powerplant as outlined in the Systems Description Section of the Aircraft Maintenance Manual.
The course also complies with EASA’s knowledge LEVEL 1 definition as contained in Regulation EU No. 1321/2014, Part 66, Appendix III Basic Knowledge Requirements;
A familiarization with the principal elements of the subject, with the objective;
(a) The applicant should be familiar with the basic elements of the subject.
(b) The applicant should be able to give a simple description of the whole subject, using common words and examples.
(c) The applicant should be able to use typical terms
This self-study online Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course will take approximately 40 hours of study. Students must pass a quiz at the end of each ATA chapter before the following ATA chapter is unlocked. A completion certificate is issued on successful completion of the course.
Course objectives: upon completion of the course, the student will be able to identify safety precautions related to the airframe, it’s systems and powerplant.
Identify maintenance practices important to the airframe, it’s systems and powerplant
Define the general layout of the aircraft’s major systems.
Define the general layout and characteristics of the powerplant.
Identify special tooling and test equipment used with the aircraft.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Our courses scale perfectly to PC, Laptop, tablet, android and iPhone. You must have an internet connection to use our courses.
STUDY TIME
Course completion time varies with the individual; however, we estimate approximately 40 hours will be required. You have 6 months to complete the course and can stop and restart at the same position with your progress saved. Once completed you will have a further 90 days to review the course.
SUPPORT
Should you require any assistance during your course, please contact us and we will assist you during normal working hours.
WHY USE OUR GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION COURSES?
Our online Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course provides an excellent solution for training engineers or company support staff, giving the required in-depth aircraft type knowledge with the advantage of distance learning.
WHY BUY FROM US?
Our Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course is designed and produced by EASA and UK CAA B1/B2 Engineers, Type instructors and Part 147 Training Managers. We ensure each course covers all relevant ATA chapters.
DETAILED COURSE SYLLABUS
The Boeing 757-200/300 RB211 & PW2000 General Familiarisation course begins with an aircraft type introduction, then covers each ATA chapter to approximately Part 66 Level 1;
ATA 00 – AIRCRAFT INTRODUCTION
Aircraft General, Aircraft Construction, Fuselage Section, Wing Centre Section, Wing Structure, Horizontal Stabilizer Structure, Vertical Stabilizer Structure, Body Stations And Sections, Zone System, Access Panel Zone Codes, Typical Service Lighting And Interphone Jacks, Aircraft General – Servicing, Aircraft General – Aircraft Jacking, Jacking – Axle Points, Levelling, Equipment Centres.
ATA 21 – AIR CONDITIONING
Cooling, Temperature Control, Distribution, Heating, Flight Compartment Controls, Air Conditioning Control Panel, Supplemental Heating Control Panels, A/C Cooling, Flow Control Cards, Pack Temperature Controllers, Standby Pack Temperature Controller, Backup Temperature Control Card, Valve and Actuator Position Indication, A/C Cooling – Component Location, ECS Bays, Wing-to-Body Fairing, and Main Gear Wheel Wells, Zone Temperature Control (ZTC) Unit, Trim Air Pressure Regulating and Shutoff Valve (TAPRSOV), Zone Temperature Indication, Valve Position Indication, Operation, Controls, Indications. A/C Primary (Zone) Temperature Control System, Main Air Distribution, Flight Deck Conditioned Air Distribution, Recirculation, Cargo Heating, Supplemental Heating System, Equipment Cooling System, Ground Crew Call Horn, Equipment Test Panel, Control Panel and Test Switch, Pressurization, Pressure Control, Automatic Pressure Controller, Cabin Altitude Control Panel, Pressure Sensor, Cabin Altitude Control Panel, Cabin Pressure Relief System.
ATA 22 – AUTOFLIGHT
Description And Operation, Automatic Stabilizer Trim And Mach Trim/Speed Stability, Autopilot (Flight Control) – Description And Operation, Autopilot Component Location, Autopilot Component Location, Autopilot Component Location, Yaw Damper System – Description And Operation, Control Panels, Yaw Damper Modules, Yaw Damper Servos, Modal Suppression Accelerometer, Yaw Damper – Component Location – Airframe, Modal Suppression Accelerometer, Yaw Damper – Component Location – Flight Deck, Yaw Damper – Component Location – Main Equipment Centre, Thrust Management System, Maintenance Monitor – Description And Operation, Maintenance Control Display Panel.
ATA 23 – COMMUNICATIONS
Description and Operation, Audio Control Panels, Radio Communication Systems, Radio Communication Systems, Hf Communication System, VHF Communication System, Selective Calling (SELCAL) System, Aircraft Communication Addressing and Reporting System (ACARS), Voice Recorder System, Fuselage Mounted Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT), Interphone Communication System, Flight Interphone System, Cabin Interphone System, Service Interphone System, Passenger Address System, Static Discharging.
ATA 24 – ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS
General Description and Operation, AC Generation, DC Generation – Description and Operation, Primary DC System, Standby System, Battery Charger System, Standby Power System, AC External Power, Bus Power Control Unit, External Power Panel, Control & Indicating, Electrical Systems Control Panel, Generator Field and Hydraulic Control Panel, Standby Power Control Panel, Component Layout.
ATA 25 – EQUIPMENT AND FURNISHINGS
Flight Compartment, Passenger Compartment, Cargo Compartments, Emergency Equipment, Seats, Accommodations, Miscellaneous Equipment and Furnishings, Passenger Compartment Linings, Service Units, Closets, Partitions, And Service Outlets, Seats, Stowage Compartments, Attendant Seats, Galleys, Lavatories.
ATA 26 – FIRE DETECTION
Fire/Overheat Detection, Extinguishing, Engine Fire Detection, Overheat Detection, AFOLTS Card, Continuous Fault Monitoring, System Tests, Flight Deck and MEC Component Locations, Engine Component Location, Engine Fire Extinguishing, Engine Fire Extinguishing – Component Location, Engine Fire Extinguishing – Operation, APU Fire Detection, APU Fire Detection, Fire Detection Loops, Attended Mode, Unattended Mode, APU Fire Detection – Flight Deck and MEC Component Locations, APU Fire Detection – Nose Landing Gear Component Location, APU Fire Detection – APU Component Locations, APU Fire Detection – Indications, APU Fire Extinguishing, APU Fire Extinguishing – Component Location, APU Fire Control Panel, P62 Right Nose Landing Gear Control Panel, APU Fire Extinguishing – Operation – Flight Deck, APU Fire Warning, Lower Cargo Compartment Smoke Detection, Lower Cargo Compartment Smoke Detection, Lower Cargo Compartment Smoke Detection – Indications, Lower Cargo Fire Extinguishing, Wheel Well Fire Detection, Wheel Well Fire Detection, Duct Leak And Overheat Detection, Lavatory Smoke Detection, Lavatory Waste Compartment Fire Extinguishing.
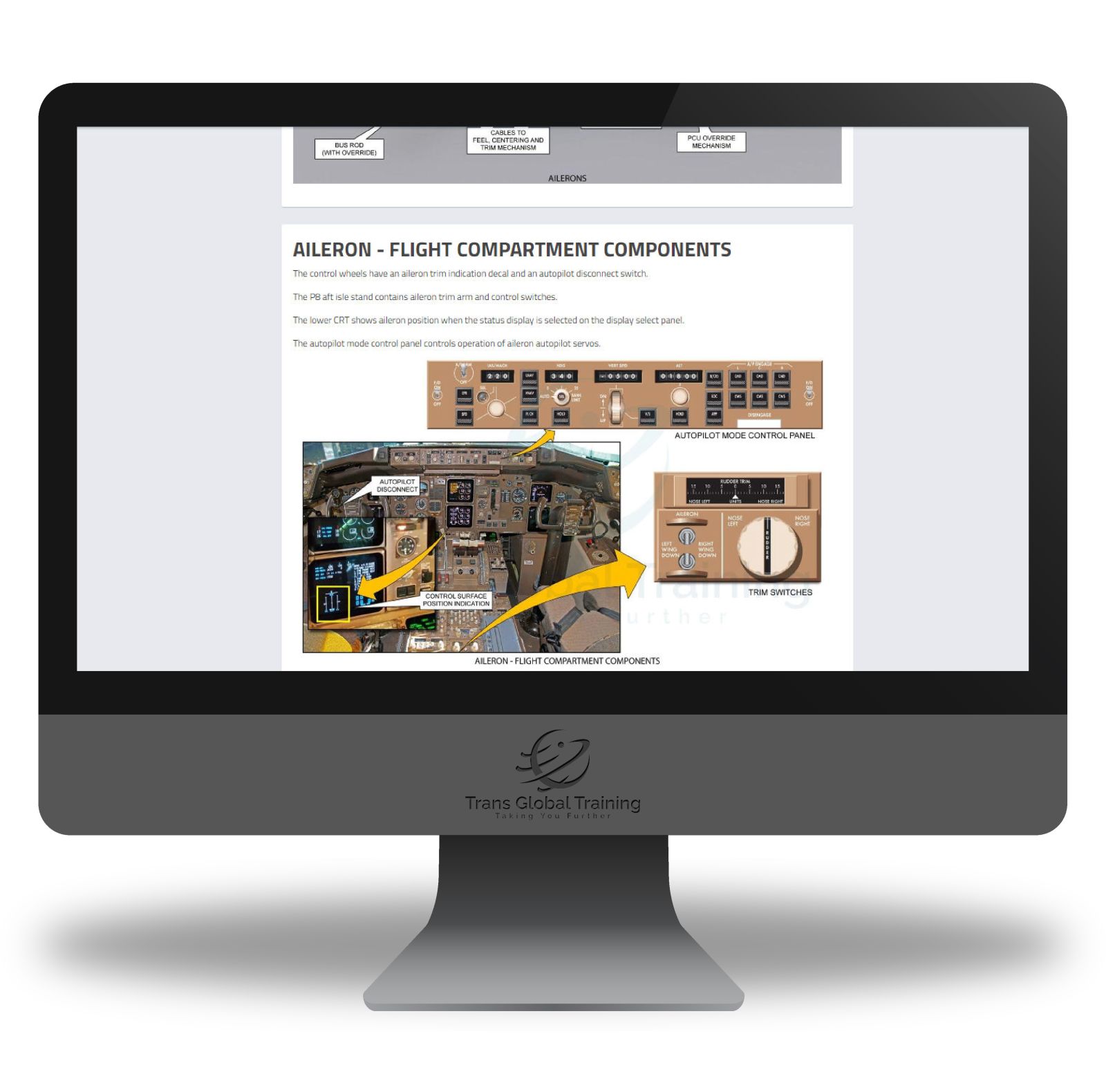
ATA 27 – FLIGHT CONTROLS
Wing Systems, Tail Systems, Flight Controls – Actuators, Servos, And Electronics, Primary Flight Controls, Secondary Flight Controls, Autopilot Servos, Control System Electronic Unit (CSEU, Flight Controls – Hydraulic Distribution, Ram Air Turbine (RAT), Power Transfer Unit (PTU), Tail Shutoff Valves, Flight Controls – Autoflight Interface, Aileron, Aileron – Flight Compartment Components, Spoilers And Speedbrakes, High Lift Control System, High Lift Control System, Primary Drive Operation (Hydraulic), Alternate Drive Operation (Electric), Trailing Edge Flaps, TE Flaps – Control And Indication, Leading Edge Slat System, Horizontal Stabilizer Trim System, Electric Trim Control, Alternate Electric Trim Control, Elevator, Pitch Control, Elevator, Stall Warning System, Rudder, Rudder, Rudder – Yaw Damper System.
ATA 28 – FUEL SYSTEMS
Fuel Tanks, Fuel Tank Vent System, Pressure Fuelling, Engine Fuel Feed, APU Fuel-Feed, De-Fuelling, Fuel Quantity Indicating and Measurement, Fuel Pressure Indicators, Fuel Temperature Indication, Fuel Measuring Sticks – Description and Operation.
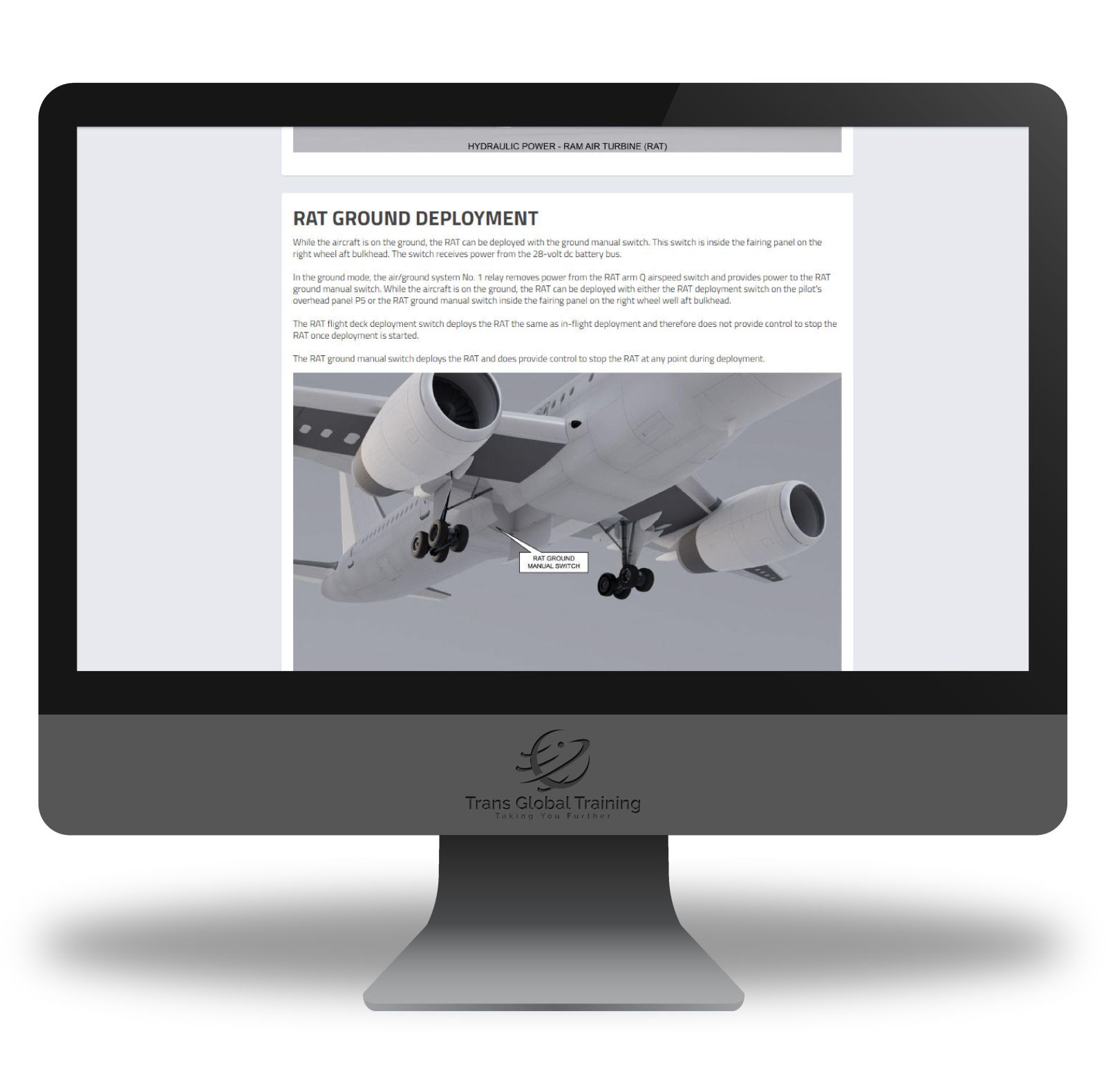
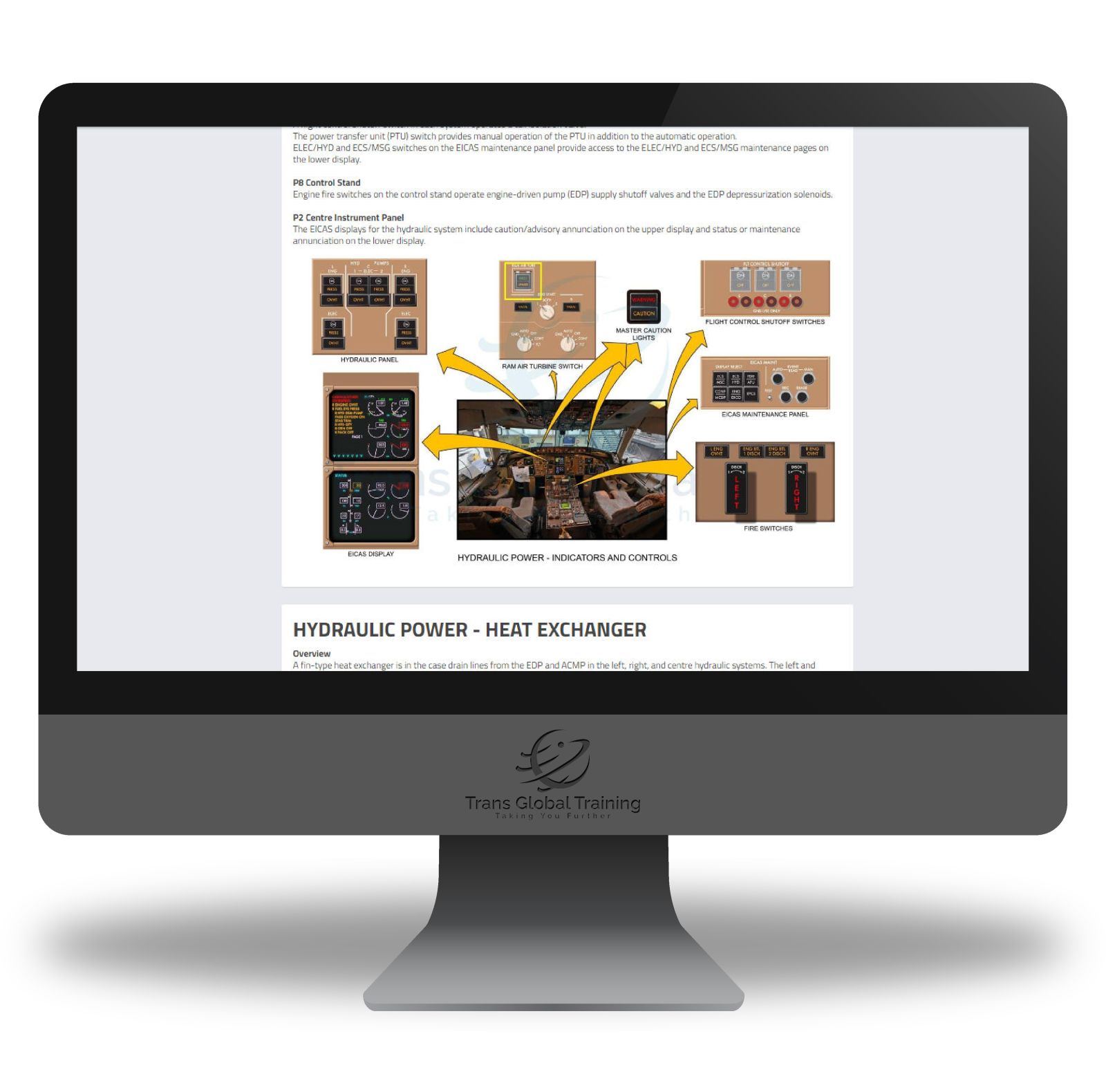
ATA 29 – HYDRAULIC POWER
System Description, Hydraulic Power – Distribution, System Redundancy, Left And Right Systems, Centre System, Hydraulic Power – System Flow, Hydraulic Power – Indicators And Controls, P5 Overhead Panel, Hydraulic Power – Heat Exchanger, Hydraulic Power – Left System Flow Schematic, Hydraulic Power – Right System Flow Schematic, Hydraulic Power – Centre System Distribution, Hydraulic Power – Ram Air Turbine (RAT), Rat Ground Deployment, Ground Servicing System, Hydraulic Fluid Quantity Indicating System, EICAS Status Messages, Safety Precautions.
ATA 30 – ICE AND RAIN PROTECTION
Wing and Engine Anti-Ice Systems, Air Data Sensor Heat, Flight Deck Windows, Drain and Water Line Heating, Wing Anti – Ice, Engine Anti – Ice, Flight Deck Control, Pitot And Static (Air Data Sensors), Pitot And Static (Air Data Sensors), Flight Compartment Window Anti – Icing, Windshield Wiper System, Water and Drain Line Heaters, Ice Detection System.
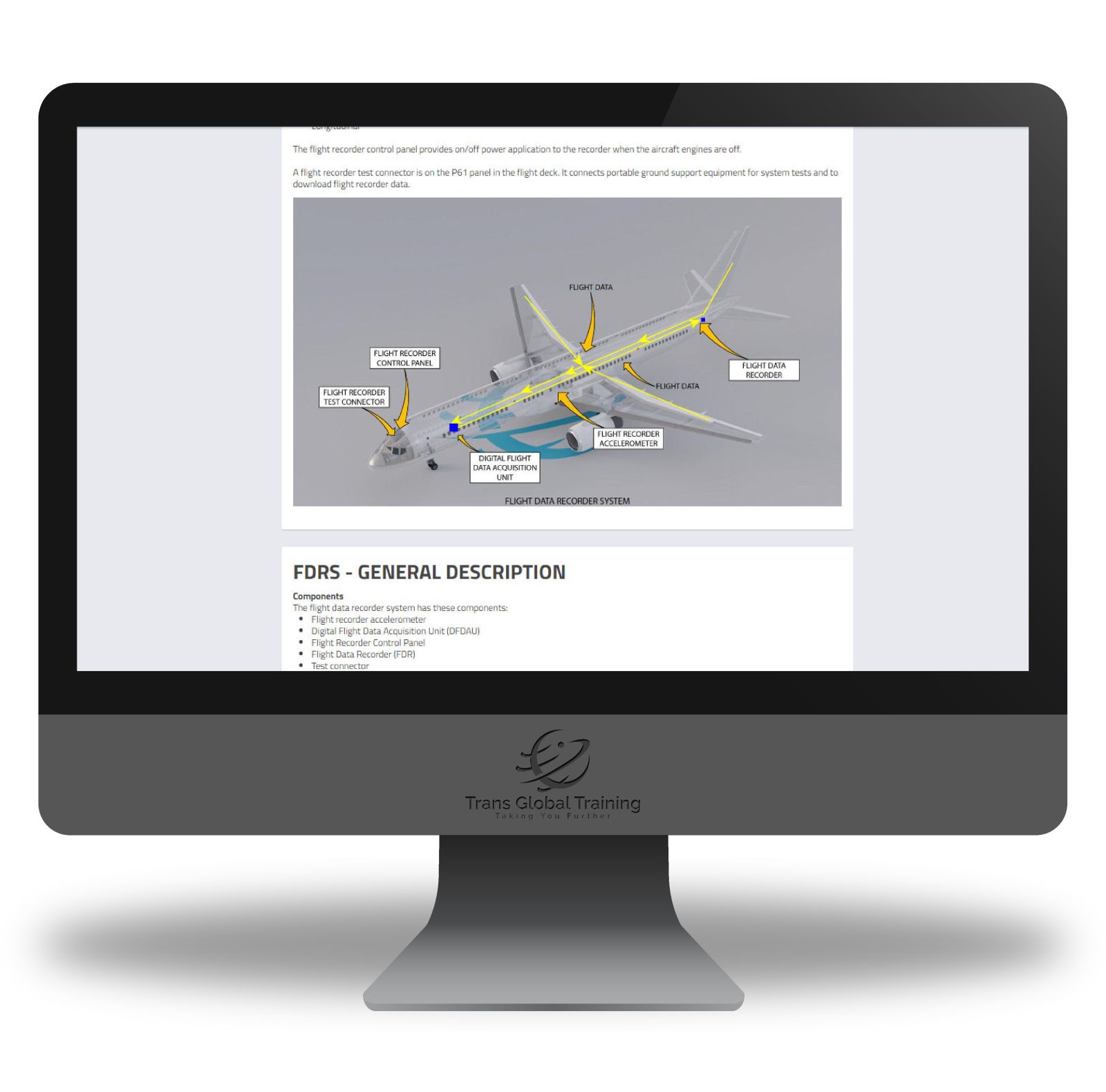
ATA 31 – INDICATING AND RECORDING SYSTEMS
Clocks, Flight Data Recorder System, FDRS – General Description, Flight Data Recording Function, Data Collection And Storage, Fault Annunciation, FDRS – Component Location – Cabin And Wheel Well, FDRS – Component Location – Flight Deck, FDRS – Component Location – Main Equipment Centre, Engine Indication And Crew Alerting System, EICAS – General Description, EICAS – Flight Compartment Component Location, EICAS – Main Equipment Centre Component Location, EICAS – Maintenance Panel, Maintenance Page Formats, Warning Electronics, Warning Electronics, EICAS Warnings, EICAS Cautions, EICAS Advisories, Warning Electronics – Flight Deck Component Location, Warning Electronics – Main Equipment Centre Component Location.
ATA 32 – LANDING GEAR
Main Gear, Nose Gear, Control and Indication, Extension And Retraction, Brakes, Antiskid, And Autobrakes, Nose Wheel Steering, Main Gear Schematic, Nose Landing Gear – Normal Operation – Alternate Operation, Nose Gear Hydraulic System Schematic, Alternate Gear Extension System, Landing Gear Door Ground Operation, Door Operation, Unsafe Lights.
ATA 33 – LIGHTS
General, Flight Compartment Illumination Control, Flight Compartment Lights, Passenger Compartment Lights, Passenger Compartment Illumination, Emergency Lights, Emergency Lighting, Emergency Lighting – Exit Signs, Service and Cargo Loading Lights, Exterior Lights.
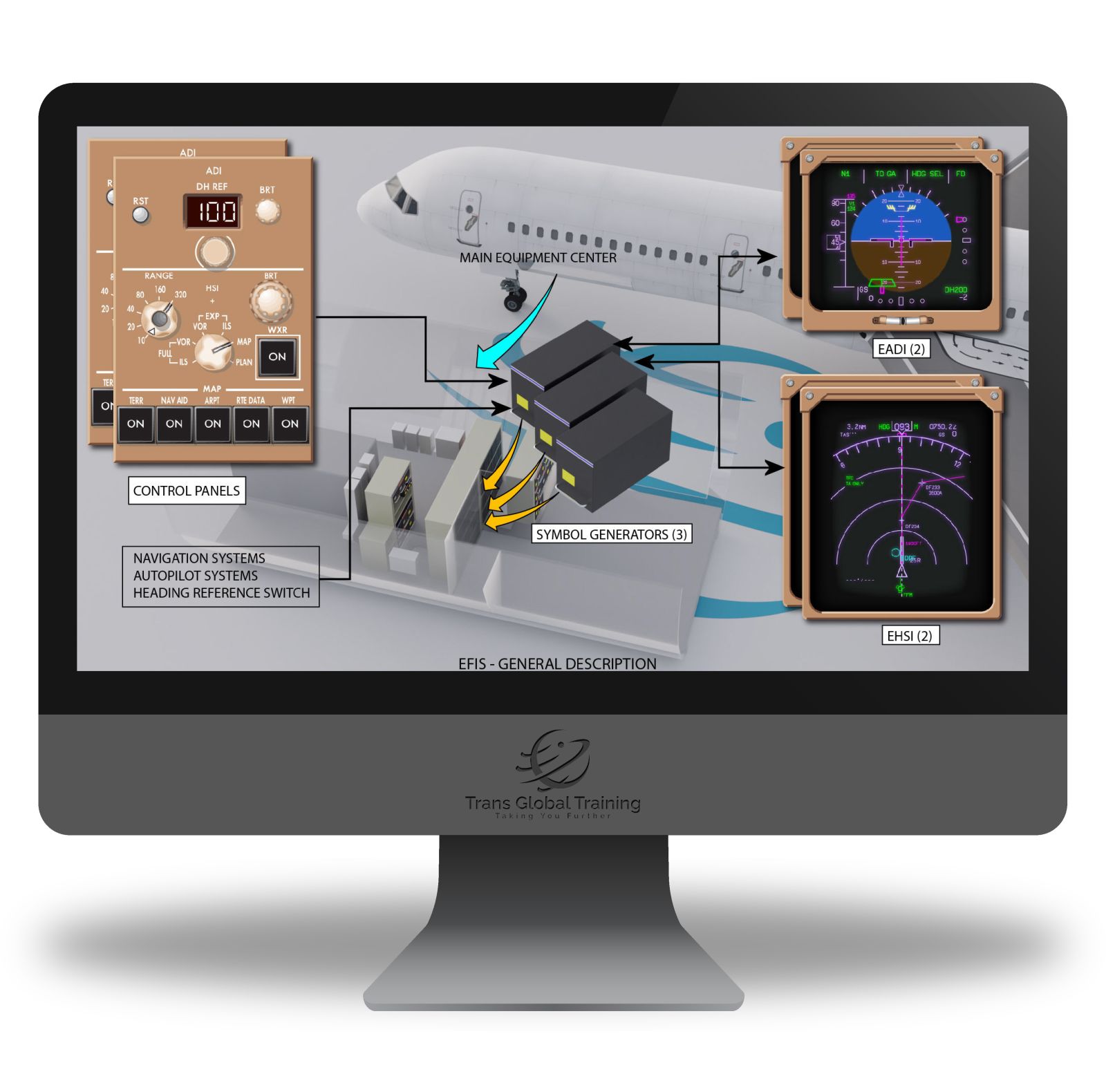
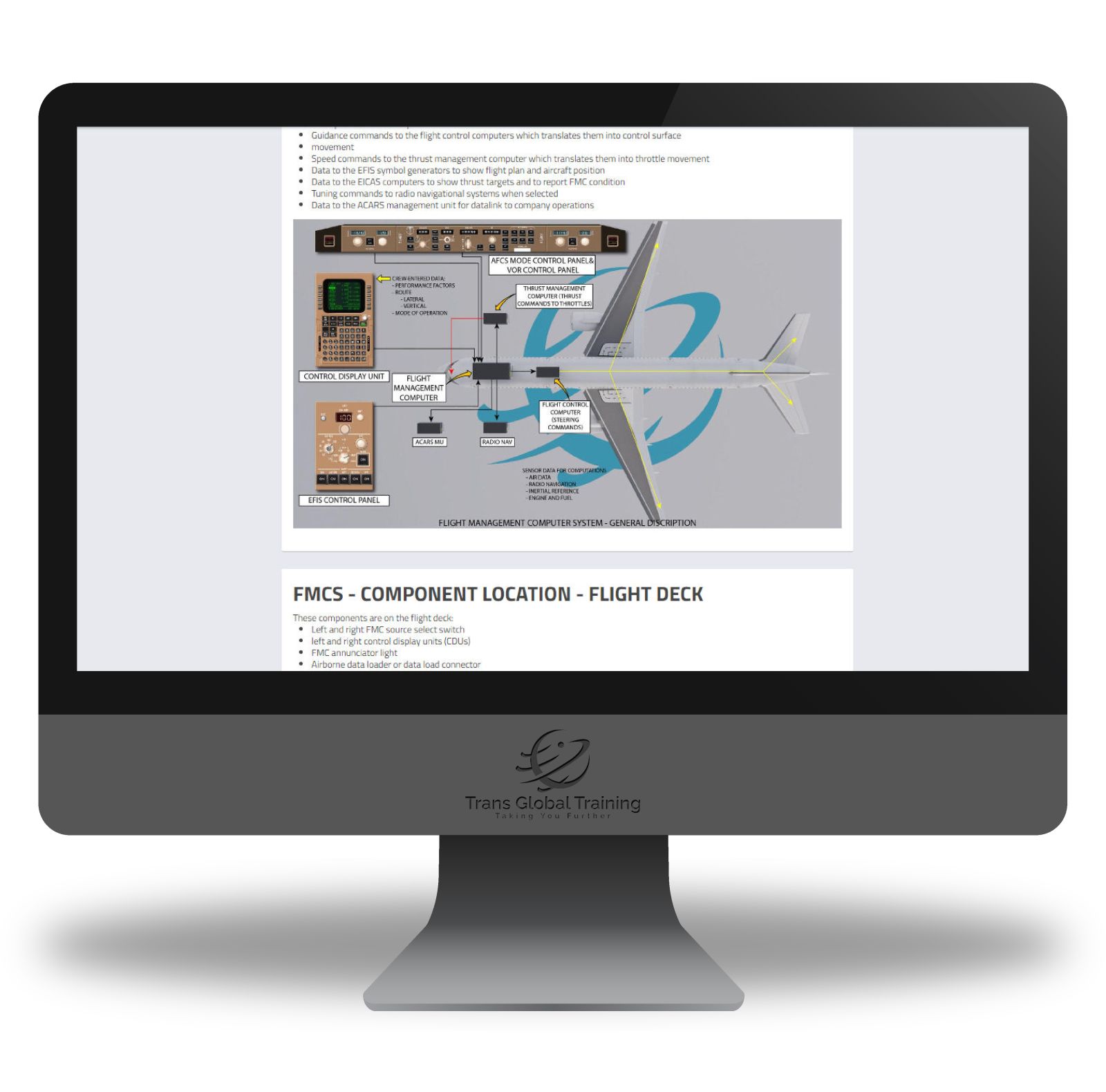
ATA 34 – NAVIGATION SYSTEMS
Electronic Flight Instrument System, EFIS – General Description, Symbol Generator, Electronic Attitude Direction Indicator, Electronic Horizontal Situation Indicator, Heading Reference Switch, Control Panel, EFIS – Component Locations, Flight Management Computer System, Flight Management Computer System, FMCS – Component Location – Flight Deck, FMCS – Component Location – Main Equipment Centre, Standby Systems, Standby Attitude/ILS Indicator, Standby Magnetic Compass, Pitot-Static System, Air Data Computing System, Air Data Instruments, Air Traffic Control System, Traffic Alert And Collision Avoidance System, TCAS – General Description, Weather Radar System, WXR System – General Description, WXR System – Component Location – Flight Compartment, WXR System – Component Location – Forward Equipment Centre And Nose Radome, Radio Distance Magnetic Indicator, Automatic Direction Finder System, ADF System – General Description, ADF System – Component Location, Vhf Omni – Range System, VOR Radials, Vor System – System Description, Marker Beacon System, Marker Beacon System – General Description, Instrument Landing System, Ils – General Description, Distance Measuring Equipment System, DME System – General Description, Radio Altimeter System, Radio Altimeter System, Ground Proximity Warning System, GPWS – General Description, Inertial Reference System, Irs – Description, Global Positioning System, GPS – Description.
ATA 35 – OXYGEN
Crew Oxygen, Component Locations, Supply and Regulation, Indications, Overboard Discharge, Oxygen Shutoff Valve/Indicator, Remote Fill Panel, Passenger Oxygen, Portable Oxygen.
ATA 36 – PNEUMATICS
Engine Air Supply, APU Air Supply, Ground Air Supply, Pneumatic Air Supply Distribution, Indication, Control, Engine Air Supply System – Rolls Royce Engines, Bleed Source Control, Temperature Control, Overheat Protection, Pressure Control, Overpressure Protection, Reverse Flow Control, Engine Air Supply System – Pw Engines, Engine Bleed Air Stage Selection, Temperature Regulation, Pressure Regulation, Reverse Flow Control, Duct Overheat Protection, Indications, APU Air Supply System, Pneumatic Ground Connector, Indicating System, Indicating System – EICAS.
ATA 38 – WATER WASTE
Potable Water System, Waste Disposal System, Water Storage and Distribution, Water Storage And Distribution, Water Heating, Water Quantity Indication, Waste Disposal – Vacuum Waste System, Waste Disposal – Vacuum Waste System, Vacuum Toilet Assemblies, Waste Tank Assembly, Gray Water Drain System, Toilet System, Waste Tank Quantity Indication, Waste Tank Quantity Indication, Water Tank Pressurization.
ATA 49 – AUXILIARY POWER
APU Engine, APU And Generator Lubrication System, APU Engine Fuel System, APU Ignition/Starting System, APU Cooling Air System, APU Bleed Air System, APU Surge Bleed System, Apu Control System, APU Exhaust Gas Temperature Indicating System, APU Tachometer System.
ATA 52 – DOORS
Passenger Entry Door System, Passenger Entry Door System – Emergency Power System, Door – Mounted Escape System, Emergency Exit Door, Cargo Door, E/E Access Door, Forward Access Door, Doors – Flight Compartment Door, Door Warning System, Door Warning System.
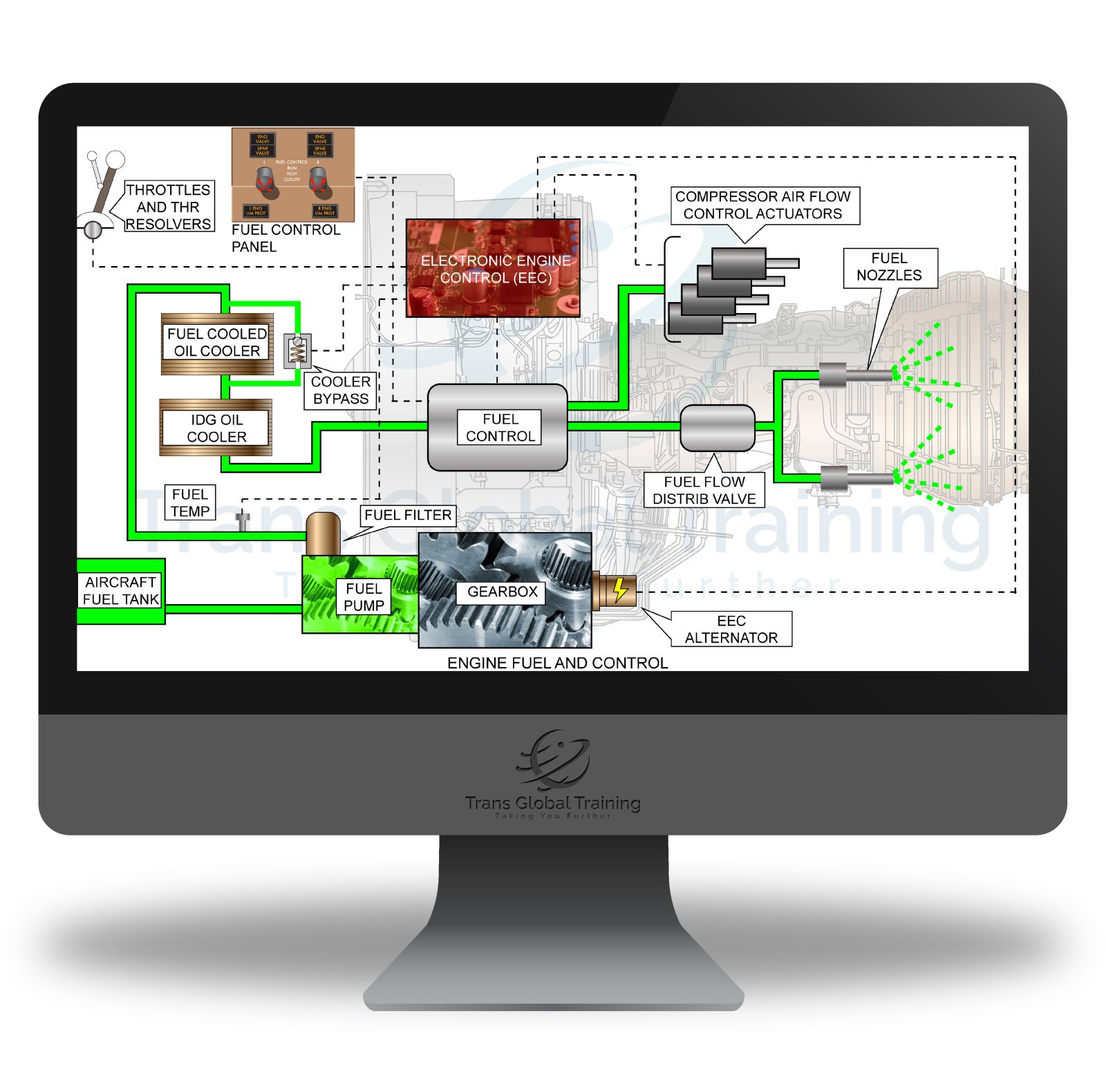
ATA 71-80 POWERPLANT – PRATT & WHITNEY PW2000
PW2000 Engine Family, Powerplant, Engine Cowling, Engine Fuel and Control, Electronic Engine Control (EEC), Fuel Control (FC), EEC Alternator, Engine External Accessories Cooling, Compressor and Turbine Cooling (CTC) System, Compressor and Turbine Case Cooling System, Turbine Vane Cooling System, Variable Vane System, Bleed System, Air Indicating System, Engine Indicating Systems, Thrust Reverser System, PW2000 Oil System, Engine Start System, Engine Ground Safety Precautions.
ATA 71-80 POWERPLANT – ROLLS ROYCE RB211
Rolls-Royce RB211, Power Plant, Engine Fuel And Control – Description And Operation, Fuel Distribution System, Fuel Control System, Electronic Engine Control (EEC), Fuel Flow Indicating System, Fuel Filter Bypass Warning System, Fuel Low Pressure Warning System, Ignition, Accessory Cooling System, Compressor Bleed Control System, Engine Controls, Engine Fire Emergency Shutdown, Turbine Overspeed Emergency Shutdown, Engine Indicating, Thrust Reverser, Deploy Operation, Stow Operation, RB211 – Oil System, Engine Starting, Engine Ground Safety Precautions.